Position of the Philippines on the global salary chart
We are WorkTime - best solution in employee monitoring for any of your business goals. In this article we will take a closer look at one of the most popular destinations for outsourcing - The Philippines . This country has become a top choice for outsourcing because of its proficient workforce and cost-effective salaries, rendering it a desirable alternative to developed nations such as the UK, Switzerland, Australia or the USA.Despite these achievements, there are skeptics who mistakenly view outsourcing to the Philippines solely as a pursuit of "cheap labor." In reality, this perception overlooks the fact that the Philippines is still a developing nation with a relatively low cost of living and expenses.The Philippines stands on par with India and its neighboring nations in terms of both cost competitiveness and service quality. This sector even received acknowledgment from the World Trade Organization in 2019 for its contribution to the Philippine economy.
Labor laws in the Philippines
If considering outsourcing tasks to the Philippines, it's crucial to understand the country's labor regulations. While many align with international standards, there are several unique to the Philippines. Here, we highlight five of the most significant ones to be aware of.1. Stability of employment
Philippine law guarantees employees job security, prohibiting unjust or unauthorized dismissals. Dismissal must follow due process, including thorough investigation of alleged incidents. Termination is only permissible for just causes, such as employee misconduct, or authorized causes like redundancy. In essence, termination without valid reasons is prohibited.2. Weekly day off
Employers must provide employees with a minimum of 24 hours of consecutive rest after every six consecutive workdays. Nonetheless, the legislation does not specifically stipulate that the rest day must fall on the weekend. With WorkTime monitoring tools, you can precisely track your employees' working hours and ensure they are not overworking. This not only prevents burnout at work but also helps comply with labor laws.By the law in the Philippines If an employee exceeds 8 hours of work within a single day, they are eligible for overtime compensation. This extra pay is set at a minimum of 25% higher than their standard hourly wage.
3. Rights to organize collectively and engage in bargaining
Collective bargaining involves discussions between employers and employees to negotiate terms on specific issues. All workers possess the right to self-organize and join unions for collective bargaining from their initial day of employment.4. Differential pay for working the night shift
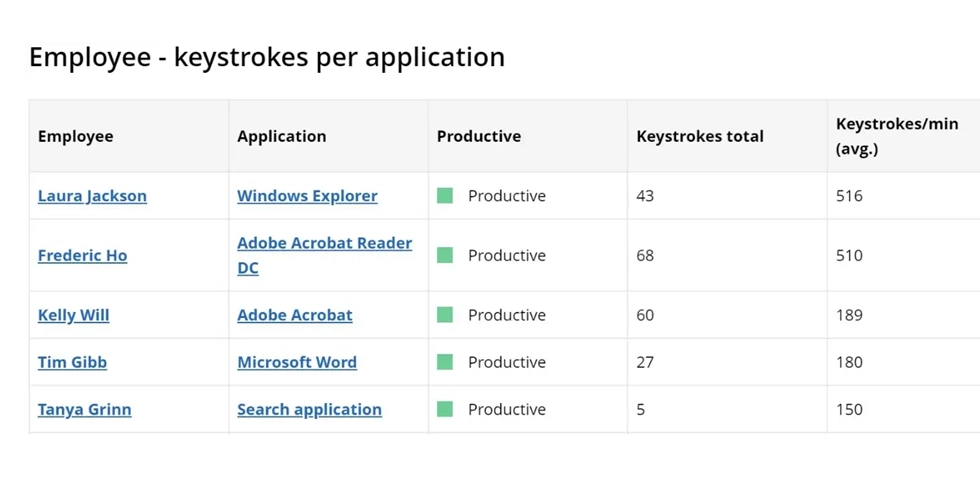
Night differential is applicable to employees working between 10 PM and 6 AM. They receive an extra 10% of their regular hourly rate for each hour worked during this period. It is easy to manage teams working in various shifts skillfully and track their effectiveness using the WorkTime reports.
5. Compensation for extra hours
If an employee exceeds 8 hours of work within a single day, they qualify for overtime pay, which is a minimum of 25% higher than their regular hourly wage. Workers who work on official holidays or rest days are eligible for premium overtime pay. They will receive their standard salary plus an additional 30% at the least.What industry does the Philippines heavily rely on?
In recent years, the Philippines has implemented significant economic reforms aimed at enhancing the business climate and attracting foreign investment. These reforms include restructuring the corporate tax system, easing restrictions on foreign ownership of micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs), and liberalizing rules on foreign ownership in specific public services.To fully capitalize on these new opportunities, foreign investors must gain a thorough understanding of the country's key industries, particularly those identified in the Strategic Investment Priority Plan (SIPP). The industries forecasted to experience significant growth in the coming years in the Philippines include:These reforms have created a more favorable environment for foreign investors, offering improved business conditions, tax incentives, and unprecedented opportunities for foreign ownership of projects, companies, and land in the Philippines.
Over 60% of the Philippines' exports consist of electronics-related products, predominantly semiconductors, with Hong Kong being one of the top export destinations.
Average salary in the Philippines and its impact on outsourcing
Based on the 2022 Occupational Wage Survey (OWS), the average monthly salary in the Philippines stands at Php 18,423.00 (US$ 330.08). Due to the absence of a national minimum wage, salaries of Filipino workers can fluctuate depending on their geographic location, industry, and skill level. Salaries in the Philippines operate under a two-tiered wage system (2TWS), incorporating both a minimum wage system mandated by Republic Act 6727, known as the Wage Rationalization Act, and a voluntary productivity-based pay scheme. Under Tier 1, the Wage Rationalization Act establishes a compulsory minimum wage per region, considering factors such as inflation, poverty thresholds, and labor force participation. Tier 2 promotes productivity-based pay, allowing for fair worker representation in defining productivity metrics and performance-based compensation. The 2TWS aims to ensure that workers can meet their basic needs while also considering the financial capacity of employers to provide wages.However, the outsourcing industry in the country provides opportunities for both undergraduates and college graduates. In the BPO sector, companies and their clients often offer a minimum monthly salary of USD 500, approximately PHP 25,500, for customer and technical support roles, with higher compensation for more specialized services.Many local and multinational companies typically mandate at least a bachelor's degree for their employees. The average starting salary for degree holders is PHP 16,379 or USD 318.58.
The cost of living in the Philippines
The cost of living in the Philippines can fluctuate significantly based on chosen lifestyle and geographic location. The cost of living encompasses the estimated monthly expenses for food, housing, healthcare, and other essential needs. NomadList provides a cost of living index to compare the living expenses in the Philippines for both locals and expatriates.The official currency of the Philippines is the Philippine peso (PHP), divided into 100 sentimos. Coins are available in denominations of 1, 5, 10, and 20 pesos, as well as 1, 5, 10, and 25 sentimos, while banknotes range from 20 to 1,000 pesos.For retirees or digital nomads, their funds may stretch further compared to those earning local salaries. For instance, while a software engineer in Manila might earn $16,190, the average salary in Singapore is $49,077.
The cost of living in Cebu is lower than in Manila, but it remains one of the pricier cities in the Philippines. For expatriates, the cost of living is $1,260, while locals spend around $869. Housing expenses for a studio apartment are $850, with dinner costing $2.90 and coffee priced at $0.67.According to NomadList, in the capital of the state - Manila expatriates have a higher cost of living compared to locals. Housing expenses amount to $943 for a studio apartment. The average cost of dinner is $5, and coffee costs $1.20.
Where does the Philippines outsource to?
The Philippines outsources to various countries, mostly to:- United States
- Australia
- United Kingdom
- Canada
- Singapore
- New Zealand
- Japan
- Europe (various countries)
- Middle Eastern countries (such as Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates)
- Other Asian countries (such as South Korea, China)
The Philippines - the outsourcing giant in the world
The Philippines has held the reputation as the premier outsourcing destination and the world's call center capital for many years. While India's outsourcing industry has also thrived over a similar three-decade span, it dwarfs the Philippines' industry nearly threefold in size. Despite facing formidable competition from India, Central America, and rapidly emerging Eastern European nations, the Philippines maintains an advantageous balance of factors including overall cost, business-friendly environment, cultural affinity, English proficiency, and diverse capabilities.Over time, demand for English-speaking workers surged, leading to significant industry growth in the 1990s. By the 2000s, the Philippines emerged as a top BPO destination in Southeast Asia, attracting multinational companies for IT and customer service outsourcing. Today, the BPO sector is a key contributor to the Filipino economy, with established outsourcing hubs across the country.Filipino outsourcing traces back to the 1970s when American companies began hiring locals for data entry tasks due to their English proficiency and low cost of living.
The father and the mother of BPO in the Philippines
Mar Roxas is recognized as a pivotal figure in establishing the business process outsourcing (BPO) industry in the Philippines during his tenure as Secretary of Trade and Industry in the early 2000s. He foresaw the country's potential as a major BPO player and spearheaded initiatives to create an enabling environment for BPO firms. Roxas championed the development of the IT-BPO Roadmap, a strategic plan aimed at enhancing the Philippines' BPO sector through infrastructure improvements, workforce training, and promotional efforts. He also played a crucial role in negotiating international agreements facilitating BPO service exports and implementing supportive regulatory frameworks. Thanks to Roxas' initiatives, the Philippines witnessed substantial growth in its BPO industry, earning global recognition as a leading BPO destination. Today, it stands as the world's BPO capital, hosting numerous multinational BPO companies.BPO regulations in the Philippines
Regulations governing the Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) industry in the Philippines primarily focus on ensuring data privacy and security, maintaining labor standards, and promoting investment. Key regulations include:Data Privacy Act of 2012
Ensures the protection of personal data processed by BPO companies, requiring adherence to data privacy principles and implementation of security measures.WorkTime employee monitoring does not record any personal information, any content, or passwords. It does not deal with any PHI.
Labor сode of the Philippines
Establishes labor standards, including minimum wage, working hours, benefits, and occupational safety and health regulations, applicable to BPO employees.Philippine Economic Zone Authority (PEZA) regulations
Provide incentives for BPO companies operating in designated economic zones, including tax breaks, simplified customs procedures, and other fiscal incentives.Telecommunications and ICT policies
Govern the provision of telecommunications services and promote the development of information and communication technology infrastructure to support BPO operations.Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) regulations
Require BPO companies to comply with corporate governance standards and financial reporting requirements.What makes the Philippines the top outsourcing destination?
Reasons for outsourcing to the Philippines include low labor costs, strong work ethics, English proficiency, 24/7 operations, flexibility, cultural alignment with Western countries, data privacy regulations, and government support. Filipino workers' dedication, proficiency in English, and ability to adapt to Western culture make them attractive for outsourcing. The government actively supports the BPO industry through legislation, education initiatives, and collaboration with industry groups. Outsourcing to the Philippines offers cost savings, skilled workers, and legal protections for businesses.What are the problems with outsourcing to the Philippines
Challenges associated with outsourcing to the Philippines may be a lot.1. Communication barriers
Despite English proficiency, cultural nuances and accents may still pose challenges in effective communication, particularly in understanding instructions or conveying complex ideas.2. Time zone differences
Operating across different time zones may lead to scheduling difficulties and delayed responses, particularly for businesses requiring real-time communication or support. WorkTime offers you the actual numbers on employee attendance, active time, and productivity, whether the employees work remotely to keep all the work done no matter time zone differences.3. Quality consistency
Variations in education, training, and work standards among employees may affect the consistency and quality of output, leading to potential issues with service delivery and client satisfaction.4. Attrition rates
High turnover rates in the BPO industry may result in recruitment and training costs, as well as disruptions in workflow and project continuity.5. Security concerns
Despite data privacy regulations, security breaches and confidentiality risks may arise due to inadequate security measures, potentially compromising sensitive information. Data safety is an important aspect of employee monitoring, and WorkTime employee monitoring software adheres to the highest data safety standards. WorkTime effectively serves industries such as health care, finance, government, defense, and security, among others. WorkTime uses AES-256 encryption. AES-256 is the most secure protocol - data cannot be encrypted unless the code is known.6. Legal and regulatory compliance
Adhering to Philippine labor laws, tax regulations, and other legal requirements may pose administrative burdens and regulatory complexities for outsourcing companies.7. Cultural differences
Cultural disparities between client organizations and Filipino workers may lead to misunderstandings, conflicts, or challenges in aligning with organizational values and norms.What is the current state of outsourcing in the Philippines
According to recent data from the IT and Business Process Association of the Philippines (IBPAP), the Information Technology and Business Process Management (IT-BPM) sector in the Philippines experienced significant growth in 2022. The industry saw a notable increase in both workforce and revenue.This surge raised the total headcount of the BPO sector to an impressive 1.57 million employees. Concurrently, the industry reported a substantial increase in revenue, reaching $32.5 billion, representing a 10.3% growth compared to the previous year's revenue of $29.5 billion.In terms of employment, the Philippine outsourcing industry added 121,000 full-time employees (FTEs) in 2022, marking an 8.4% growth compared to the previous year.
Top 5 outsourcing cities in the Philippines
Top outsourcing destinations in the Philippines include big cities of the state.Manila
Manila, the capital and primary city of the Philippines, serves as the focal point for the nation's economic, political, social, and cultural affairs. With a rich history spanning four centuries, Manila has long been a key driver of industrial progress in the country. Renowned as the top outsourcing hub in the Philippines, Manila holds significant importance in the global outsourcing landscape. It currently holds the eighth position on Tholons' supercity list, which ranks cities as attractive destinations for technology, digital innovation, and business process management.Cebu City
Cebu City, known as the oldest settlement in the Philippines, holds significant historical importance and preserves its Spanish heritage. Drawing over 2 million tourists annually, it stands as one of the country's most visited destinations. Moreover, Cebu has emerged as a prominent outsourcing hub, with numerous business centers and multinational corporations establishing operations in the region. This has propelled Cebu to the 52nd position on Tholon's supercities list, highlighting its attractiveness as a destination for business process management and digital innovation.Davao City
Davao City serves as the primary hub for trade and commerce in Mindanao, the southernmost island group of the Philippines. It consistently ranks at the top of the Next Wave Cities list curated by the Department of Information and Communications Technology (DICT) of the Philippines. This list identifies urban centers with the capability to accommodate significant business process outsourcing (BPO) and information technology (IT) firms.Santa Rosa Laguna (Metro Laguna)
Santa Rosa, Laguna, the second-largest city in Metro-Laguna, is situated approximately thirty kilometers away from Manila. As of the 2021 census, it boasts a population of 332,521 residents. Classified as a first-class municipality, Santa Rosa administers thirty-six barangays within its jurisdiction.Bacolod City
Bacolod City, located in Negros Occidental, is renowned for its sugar industry and is recognized as the first capital of the Philippines. It is also famous for the globally acclaimed Bacolod Chicken Inasal. Considered an economic hotspot in the Philippines, Bacolod City has witnessed significant growth in its outsourcing industry over recent years. With over 100,000 business process employees, it hosts various sectors including electronics assembly, customer service call centers, and other IT-enabled services. The city is home to Negros First CyberCentre, a cyber park designed to provide an optimal environment for information and communications technology business process outsourcing investments. Spanning across a four-hectare lot, this three-story commercial building accommodates IT BPO companies alongside various food, retail, health and wellness, and travel service establishments.The first outsourcing company in the Philippines
In 1992, outsourcing commenced in the Philippines with the establishment of the country's inaugural contact center, the Accenture Global Resource Center, by Frank Holz. Initially, these pioneering contact centers offered fundamental services like email response and service management. During the presidency of former President Fidel V. Ramos, the Philippine Economic Zone Authority (PEZA) was established. This agency is dedicated to aiding foreign investors in streamlining their business activities within designated regions across the country.Two years later, former employees of a multinational management consulting firm, Jim Franke and Derek Holley, established eTelecare, which is famously recognized as the country's premier call center. In 2010, the Philippines earned the title of the global hub for Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) when it employed 525,000 individuals and generated $8.9 billion in revenue.In 1997, Sykes Asia became the inaugural multinational Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) company in the Philippines.
What are the big 4 BPO companies in the Philippines?
The "big four" BPO companies in the Philippines typically refer to the largest and most prominent players in the industry. While rankings may vary depending on specific criteria, the following companies are often considered among the top BPO firms in the Philippines:1. Concentrix
Concentrix is one of the leading providers of customer engagement services and technology solutions worldwide, with a significant presence in the Philippines.2. Teleperformance
Teleperformance is a global leader in outsourced customer experience management, operating numerous centers in the Philippines and serving clients from various industries.3. Accenture
Accenture is a multinational professional services company offering a wide range of services, including consulting, technology, and outsourcing. It has a substantial BPO presence in the Philippines.4. Sykes Enterprises
Sykes Enterprises is a multinational BPO company providing customer engagement services, technical support, and other solutions. It is one of the largest BPO employers in the Philippines. These companies are known for their extensive operations, global clientele, and significant contributions to the BPO industry in the Philippines.Employee monitoring in the Philippines
To effectively manage a team on outsourcing in the Philippines, clear control over all processes outsourced by the company is essential. This will be facilitated by employees monitoring. WorkTime has extensive experience in assisting clients in controlling and effectively managing processes, both in-house and outsourced. Therefore, we have identified five key points that will help build successful outsourcing in the Philippines. 1. Monitor the time spent by your BPO staff on assigned tasks. Compare employee active time between remote and in-office work. With WorkTime, you can skip the guesswork and compare the actual numbers.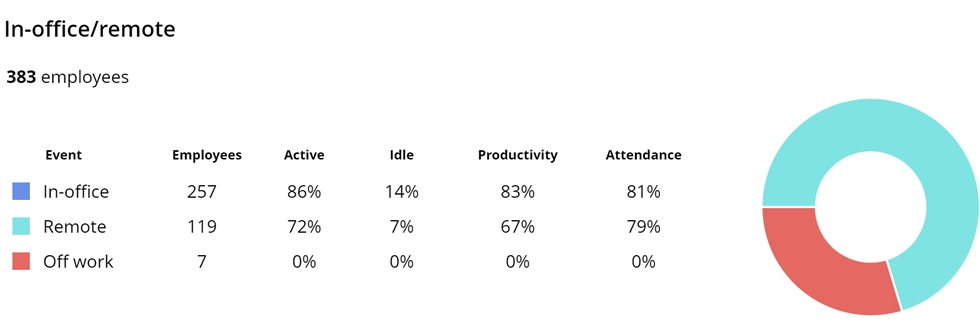

WorkTime tracks and compares employee performance across multiple offices. Instead of relying on assumptions, you can make informed decisions by analyzing attendance, active time, and productivity by location.
Start free trial